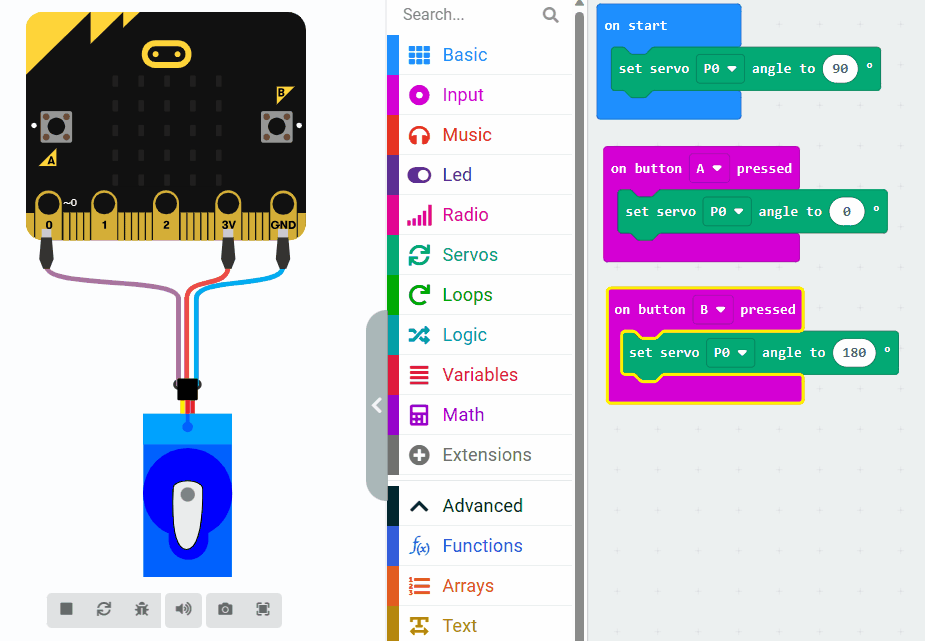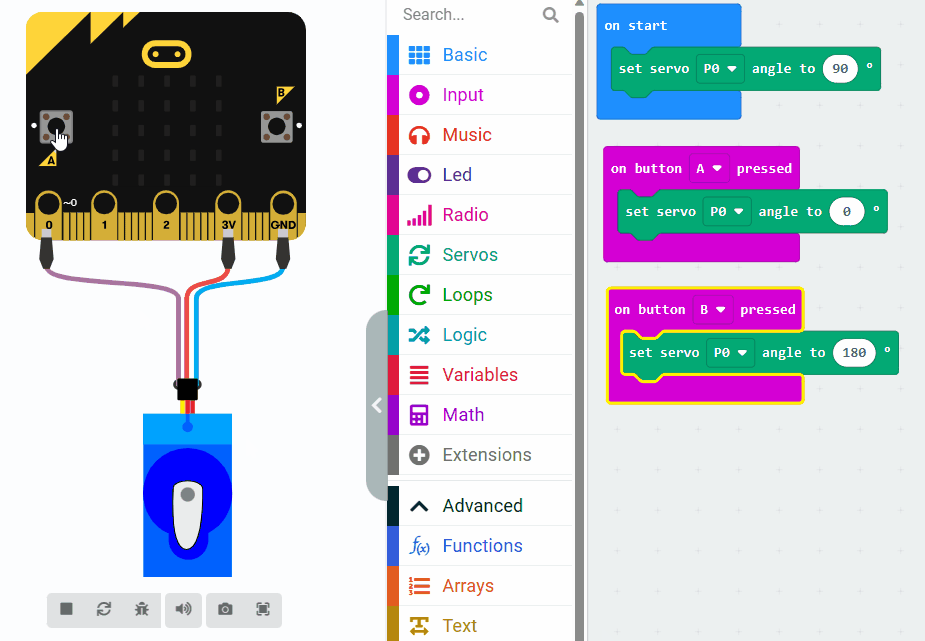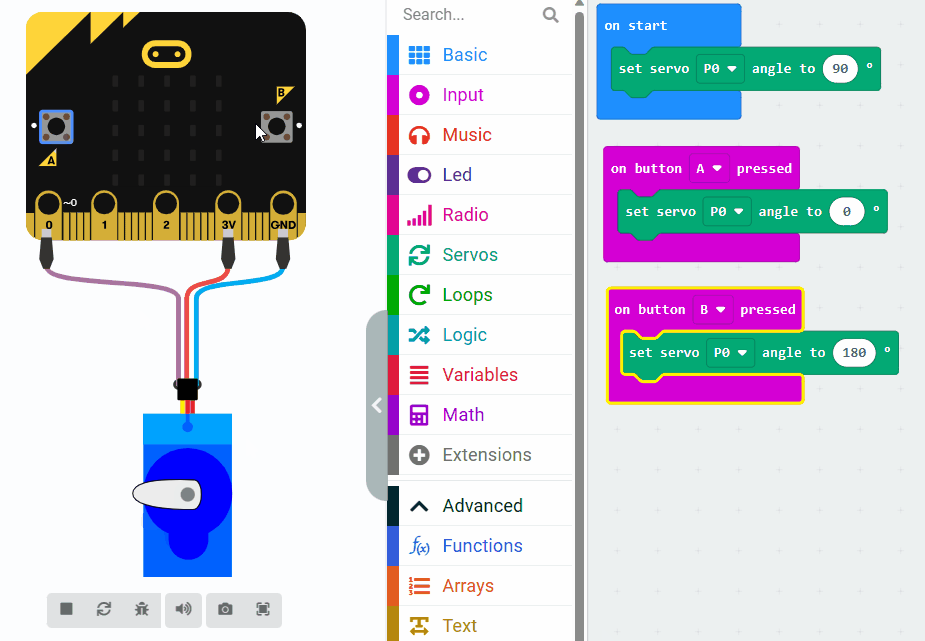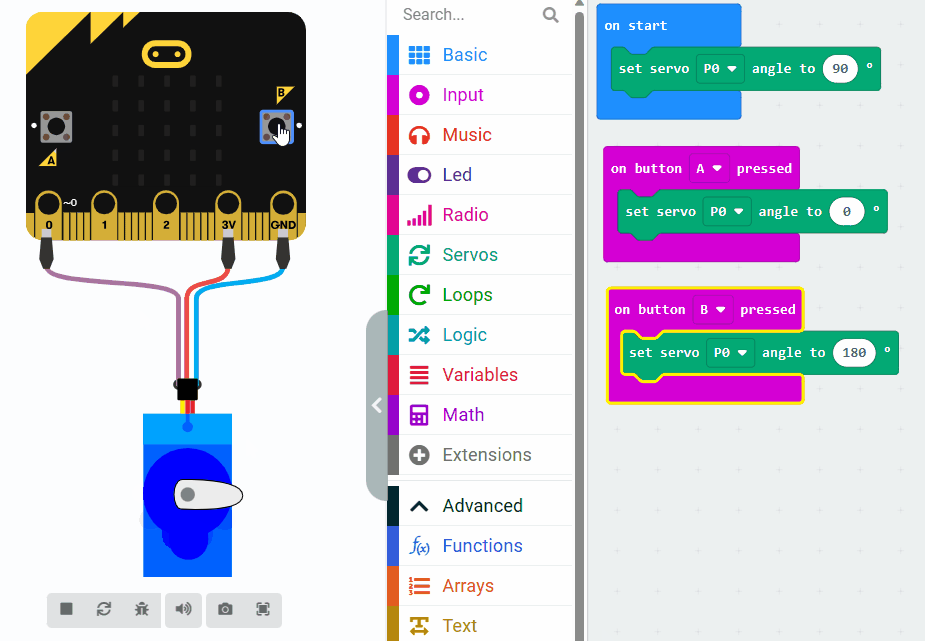
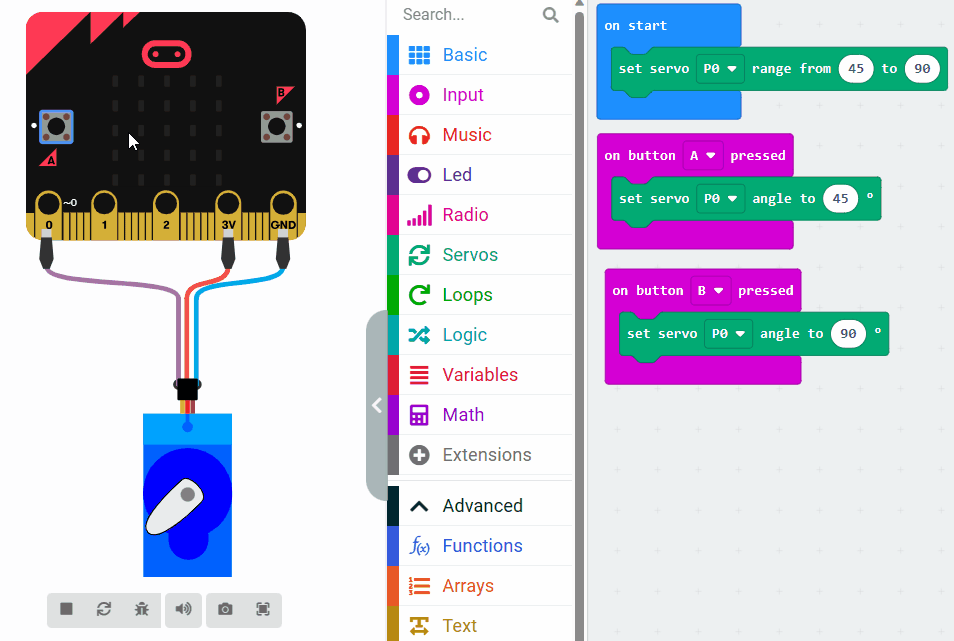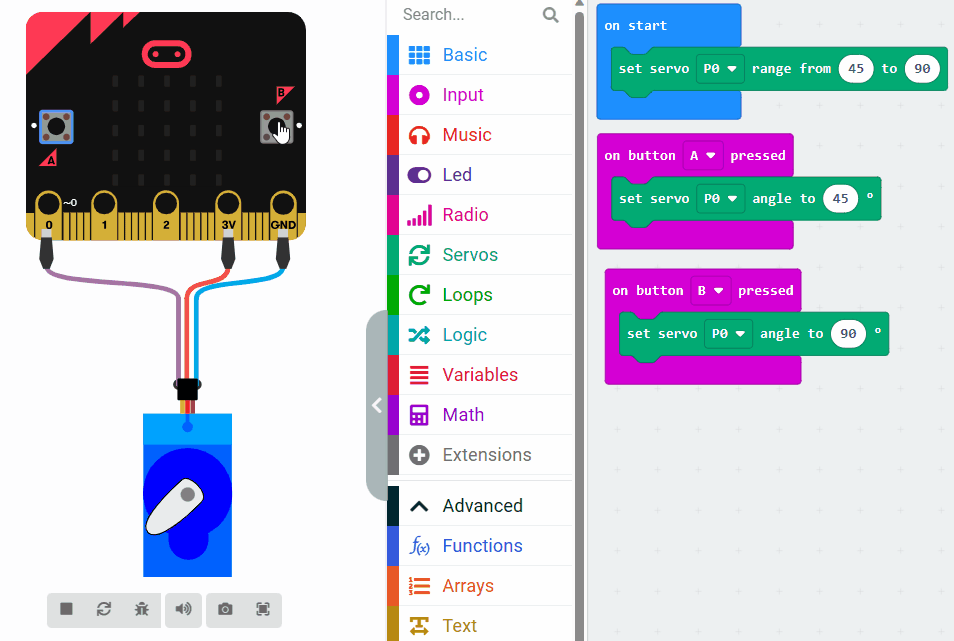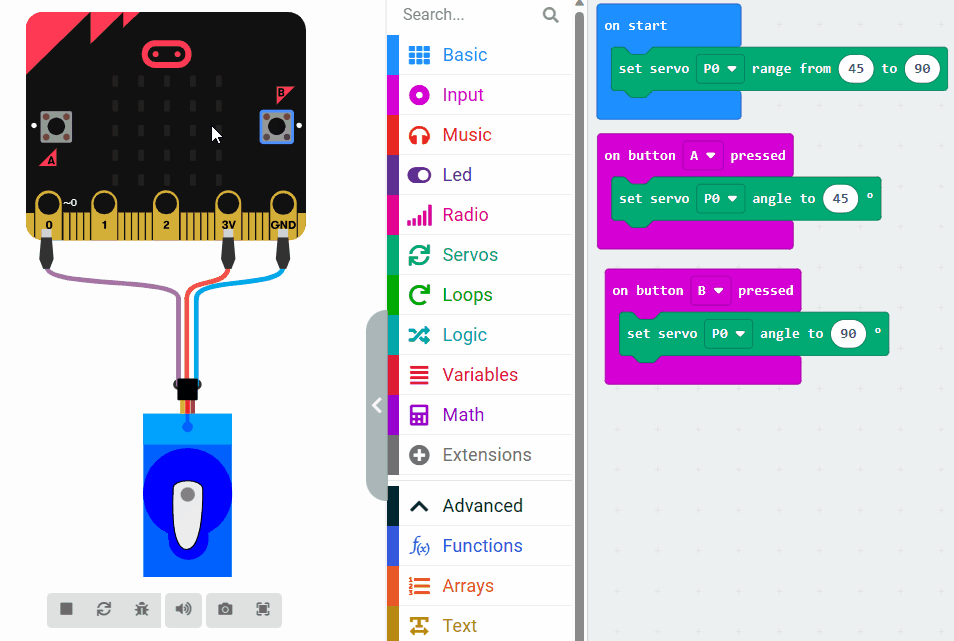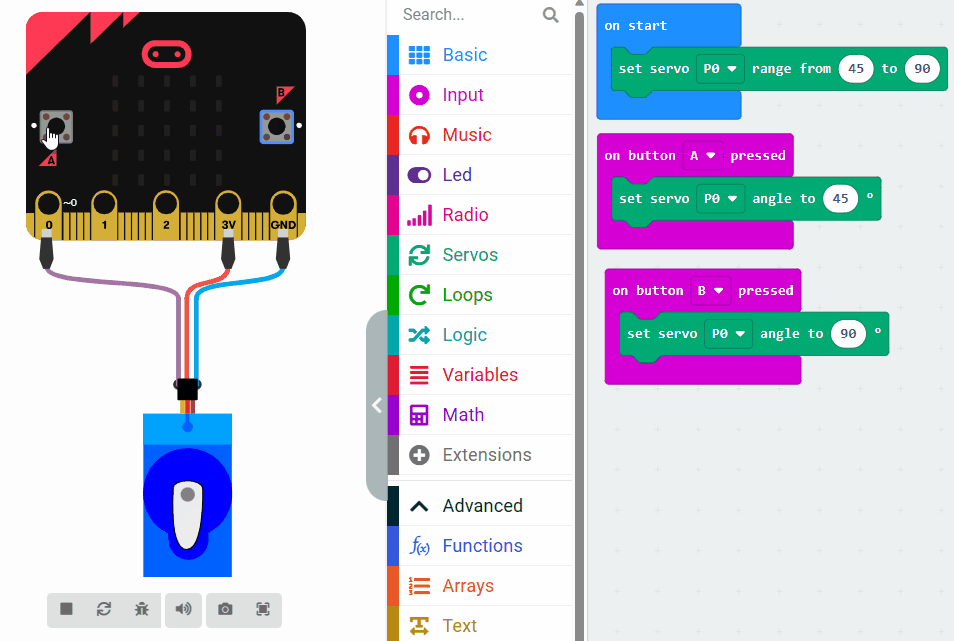
Servo motors are a type of motor that can be controlled to move to a specific angular position. They are commonly used in robotics for tasks such as steering and controlling robotic arms. In this lesson, we will learn about the concepts and techniques for programming a servo motor.
Servo motors typically use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signals to control their position. PWM signals consist of a series of pulses with varying widths. The width of the pulse determines the desired angular position of the servo motor.
To control the servo motor's position, you will write code that sends specific signals to the motor. These signals are in the form of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signals, which are a series of pulses with varying widths. The width of the pulse determines the position of the servo motor.
In this example, we set the servo motor to a neutral position (90 degrees) initially. When button A on the Micro:bit is pressed, the servo motor will move to 0 degrees, and when button B is pressed, it will move to 180 degrees. This will be achieved by sending appropriate PWM signals to the servo motor through the Micro:bit's pins.
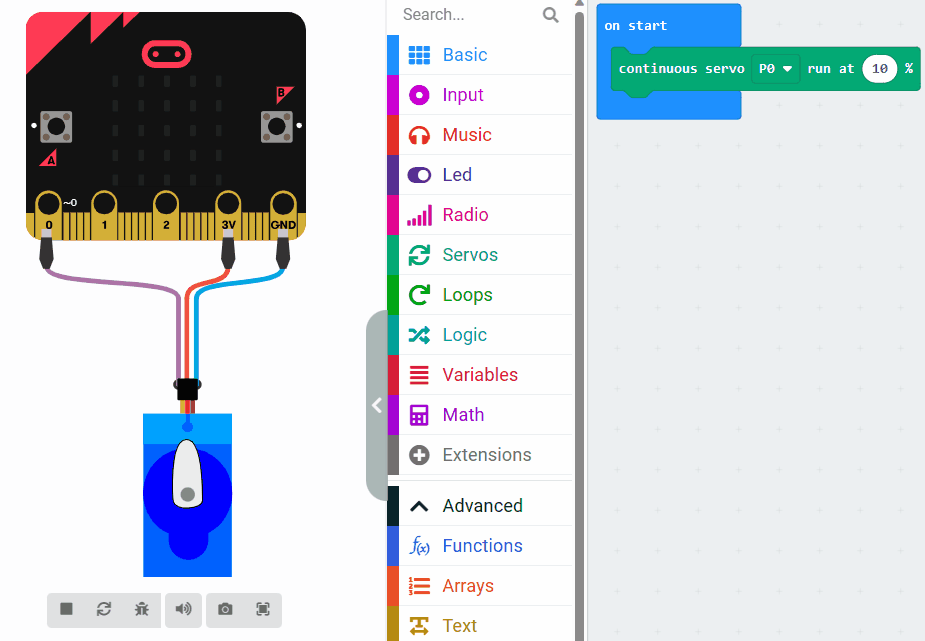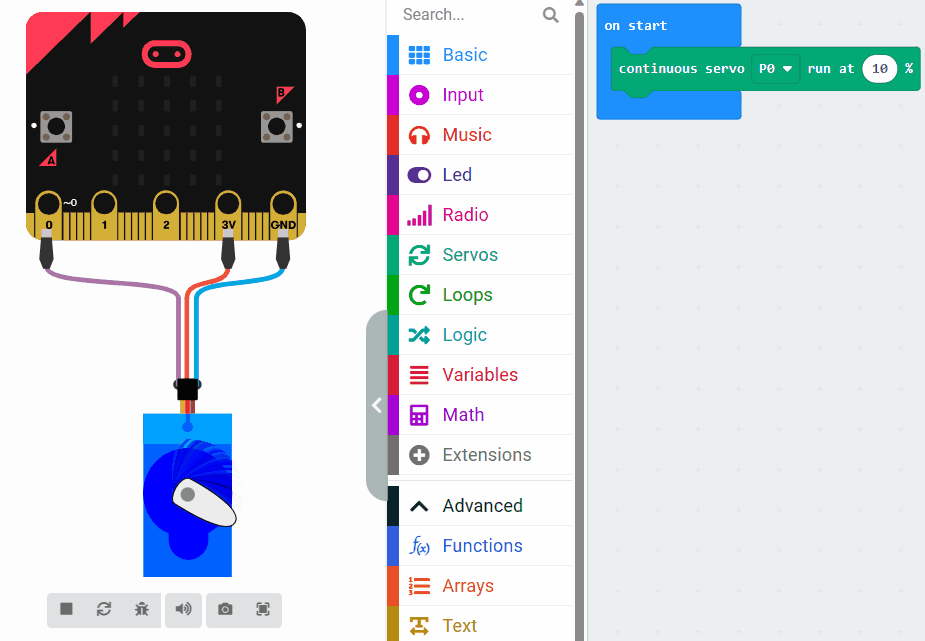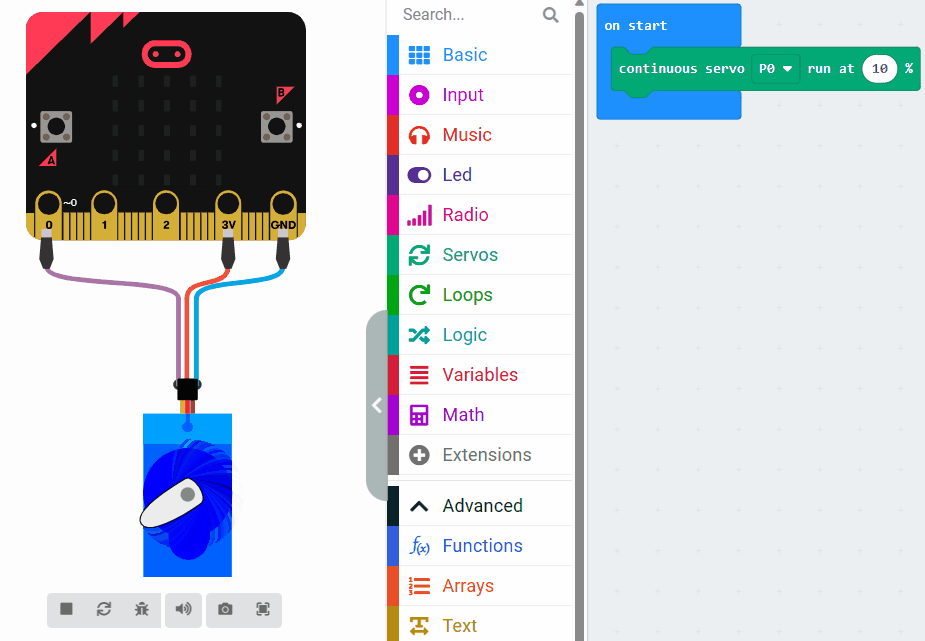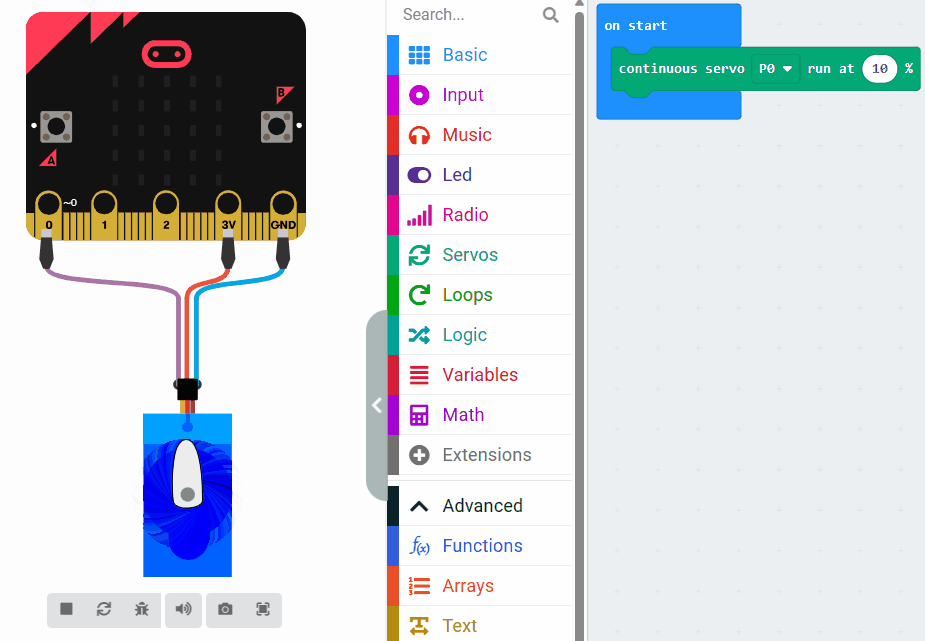
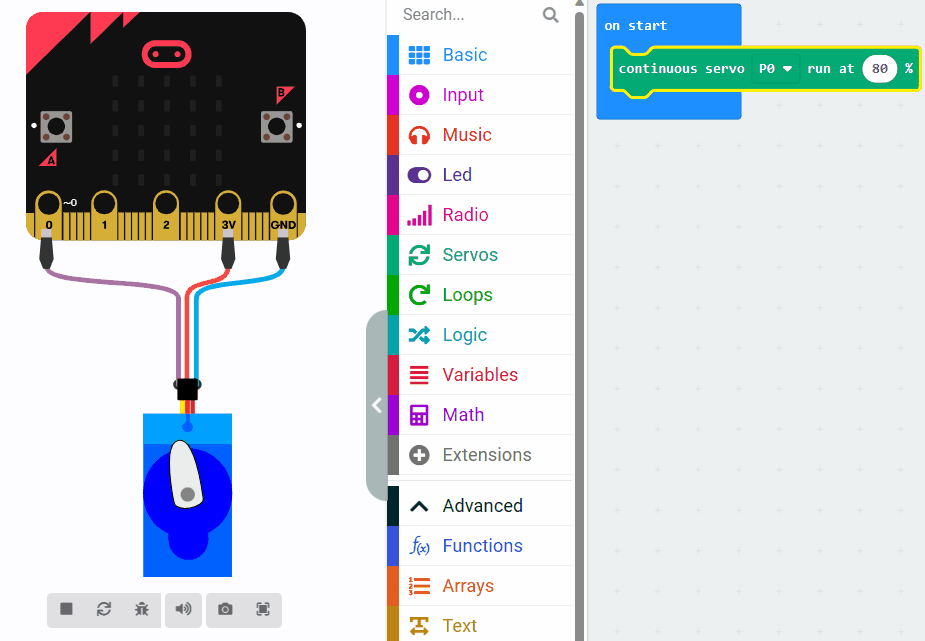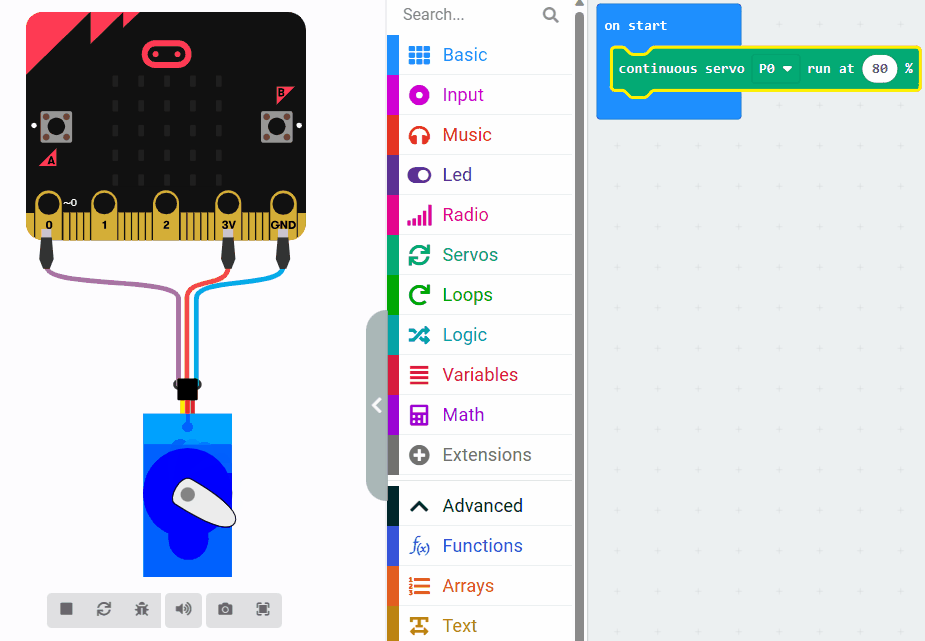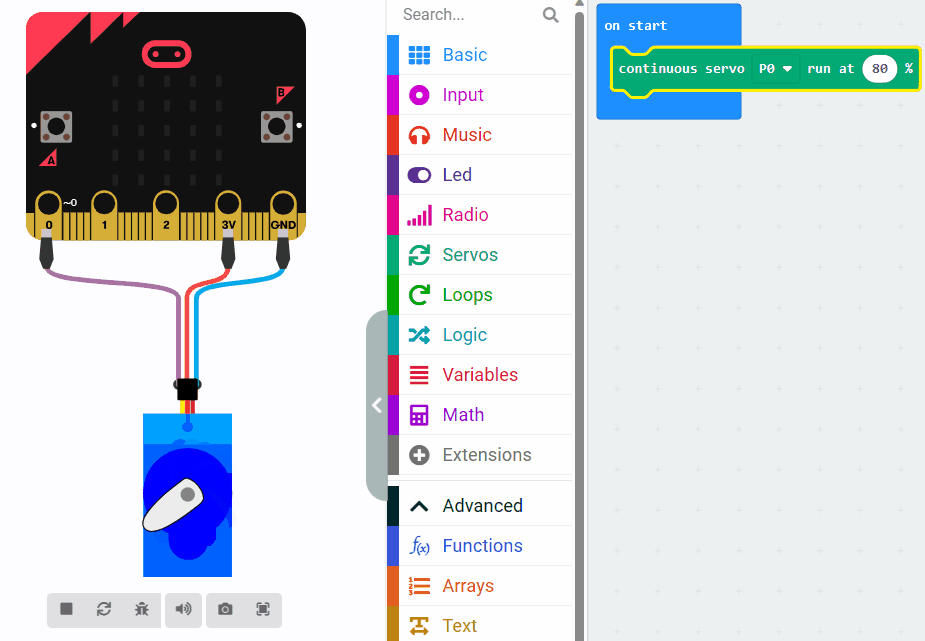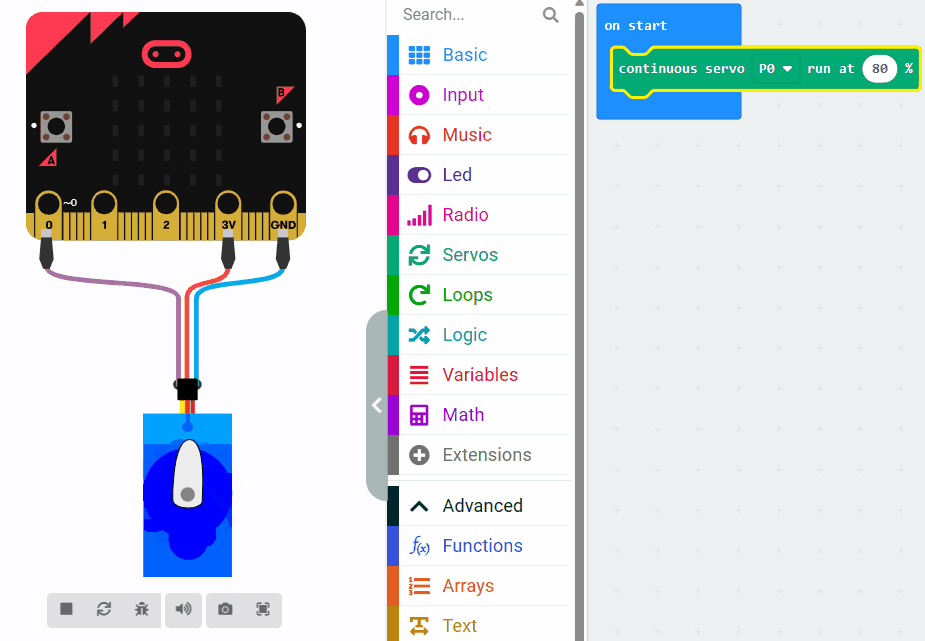
Now let's learn about servo speed and how it affects the movement of a servo motor. Observe the difference in speed by looking at the two images.
The first image sets the speed to 10% and the second sets the speed to 80%.
By controlling the speed of a servo motor, you can achieve smoother and more precise movements in your projects.
If you want to limit the rotation range of a servo you can set it’s minimum and maximum rotation angle. The minimum angle limit is set in degrees from 0 to 90. The maximum rotation angle is set in degrees from 90 to 180.
Let's understand the given code snippet: