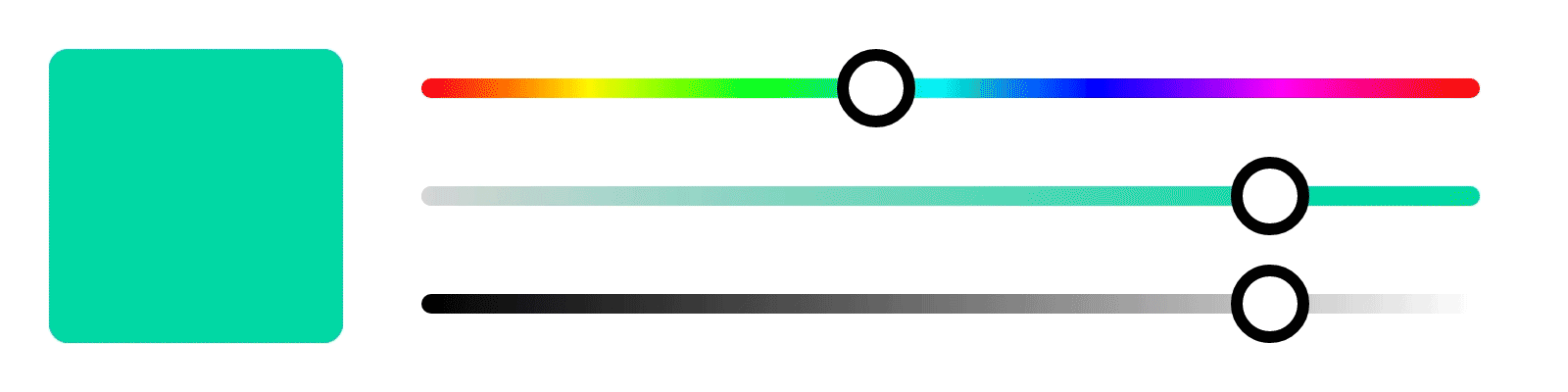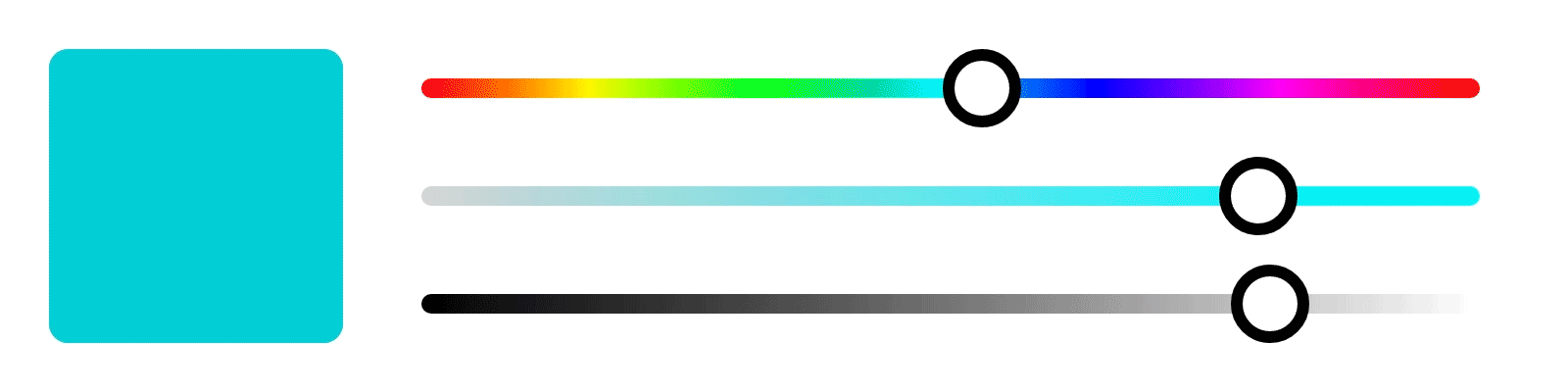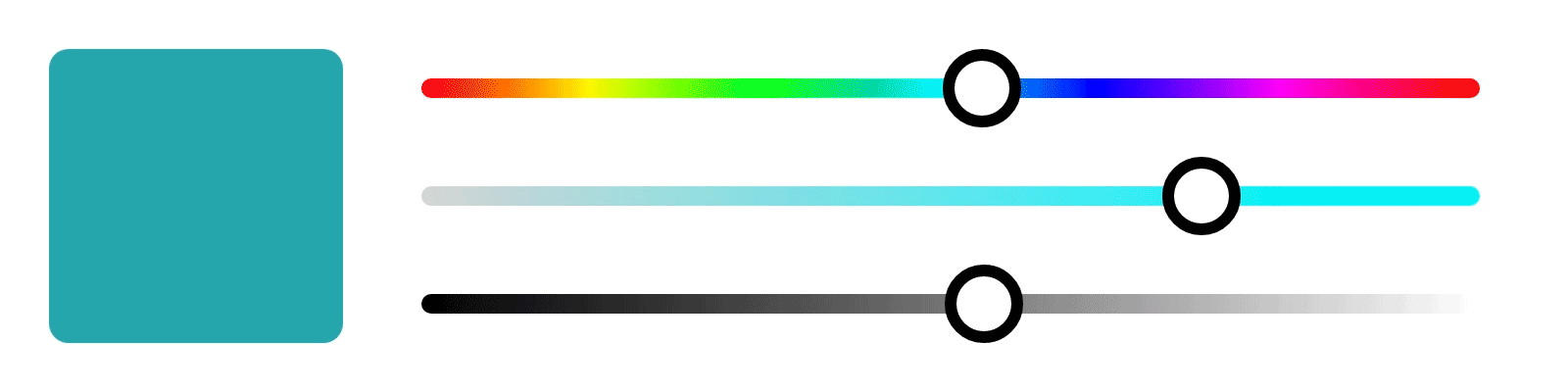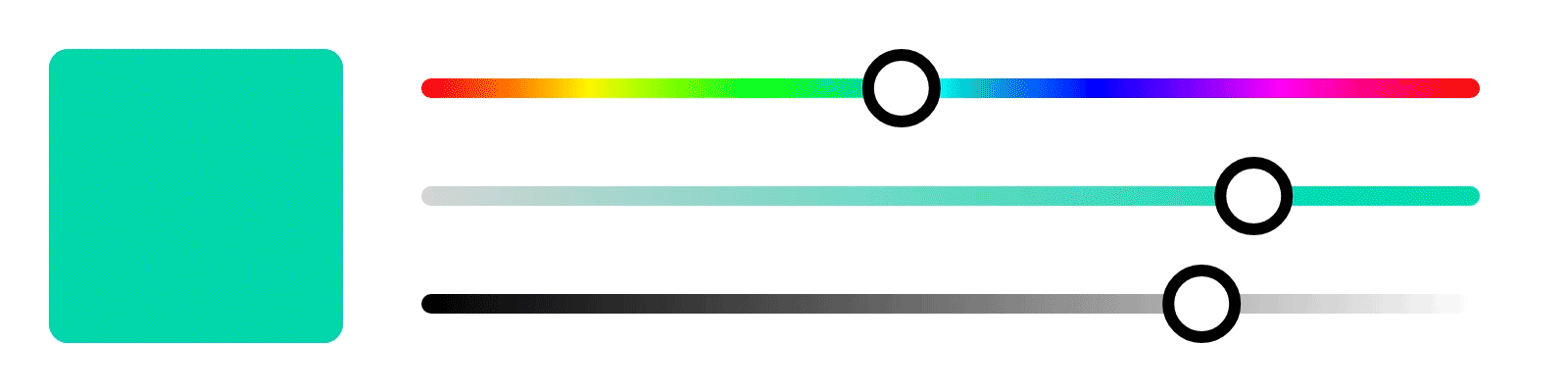Color is a fundamental element in the world of art and design. Understanding color theory is essential for creating visually appealing artwork. In this lesson, we will introduce you to the basics of color theory and how to apply it to your digital art.
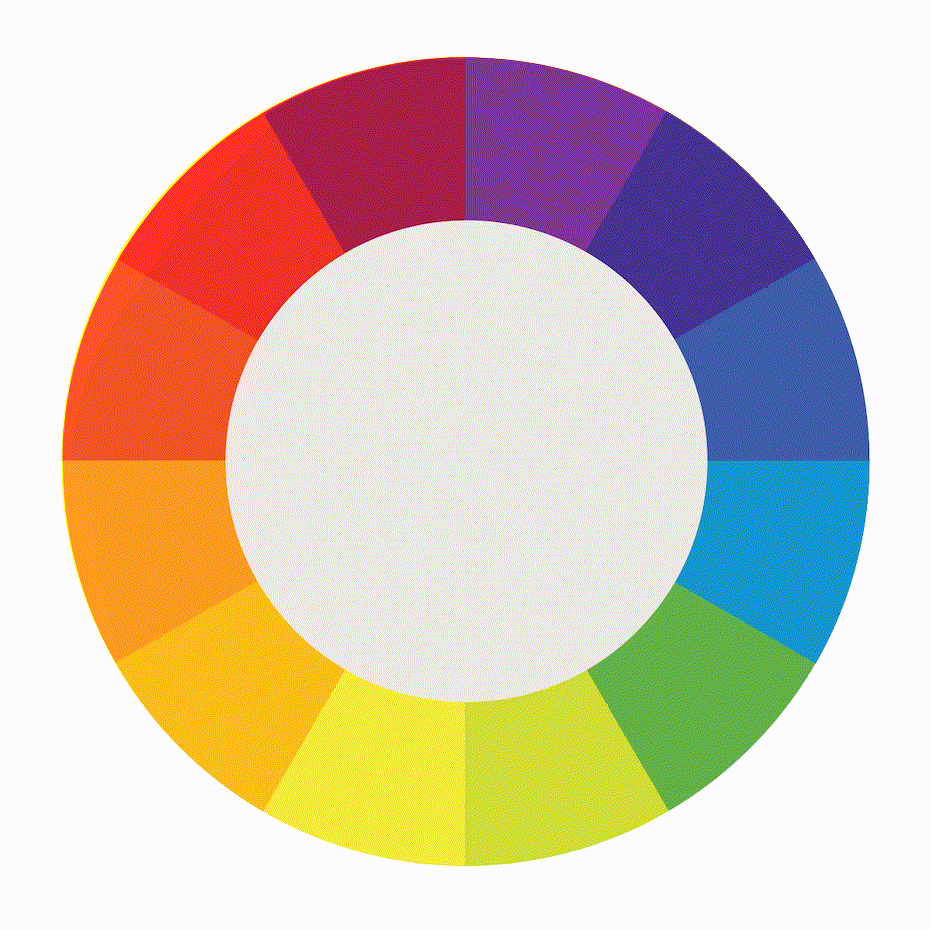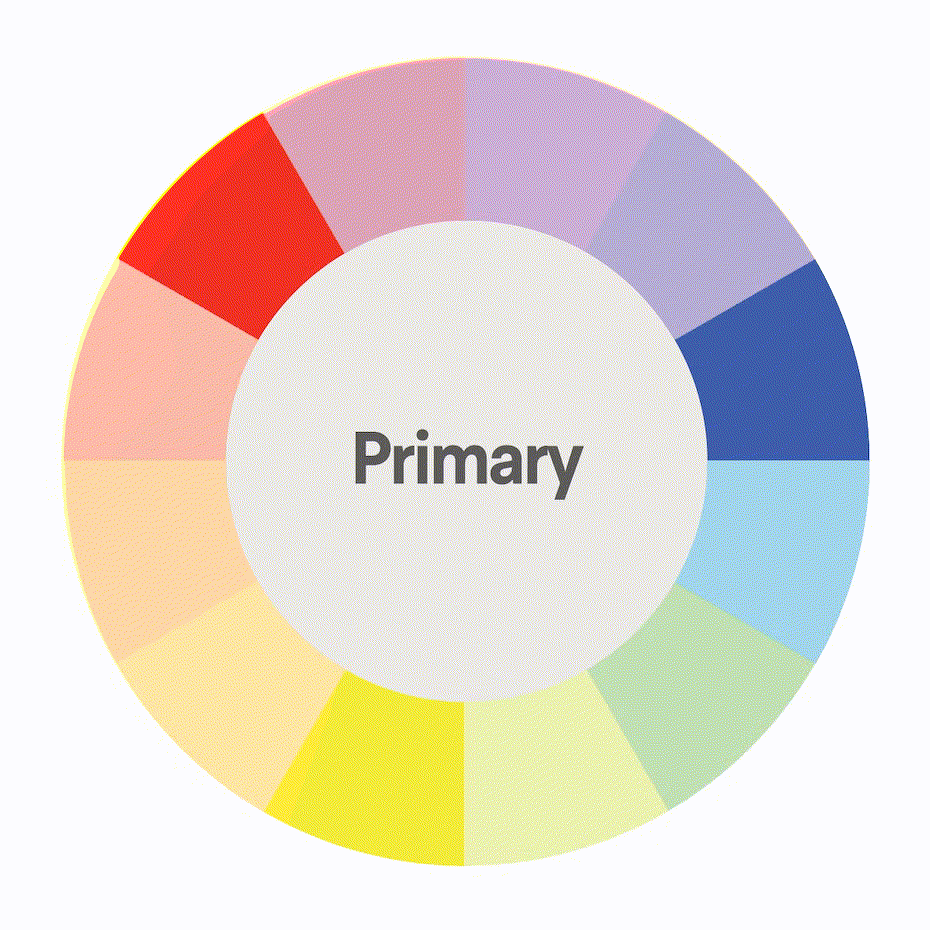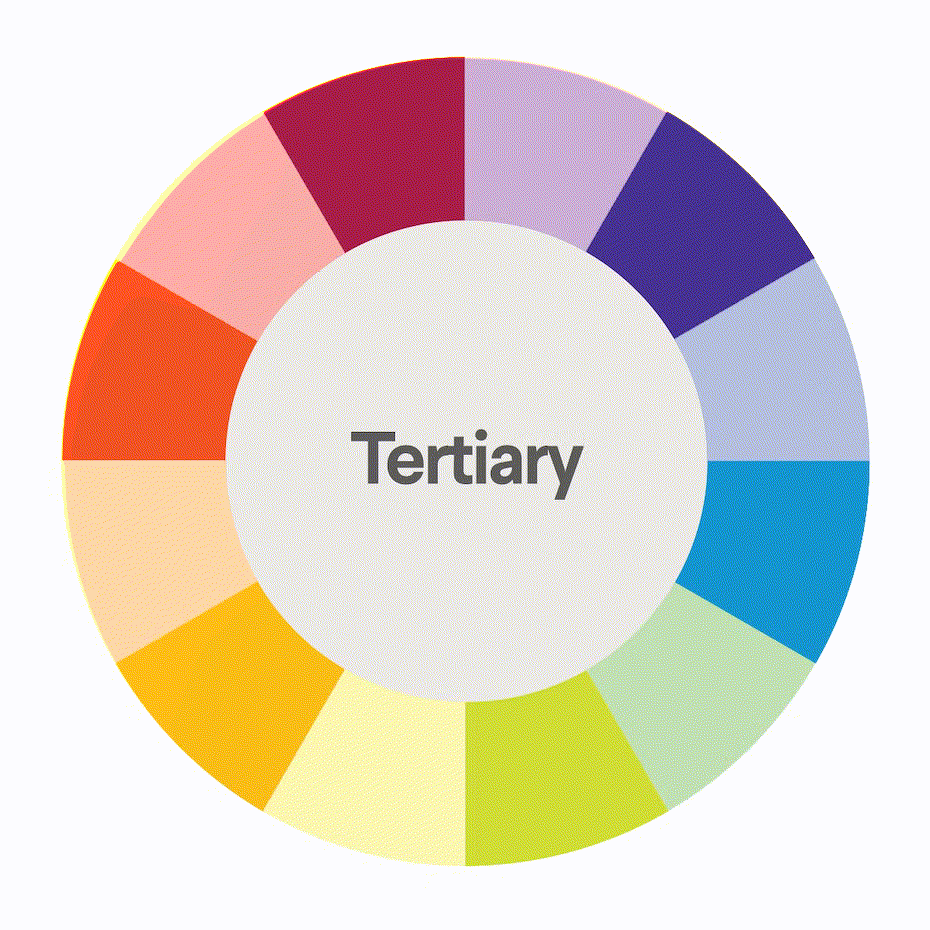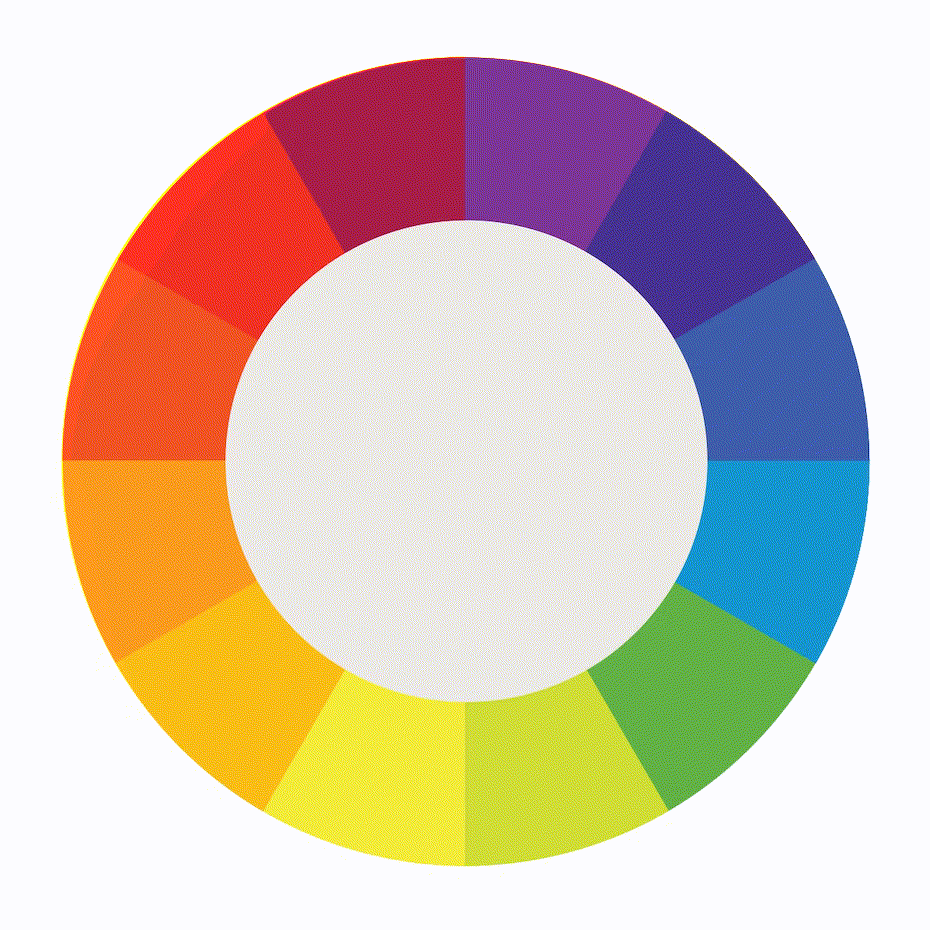
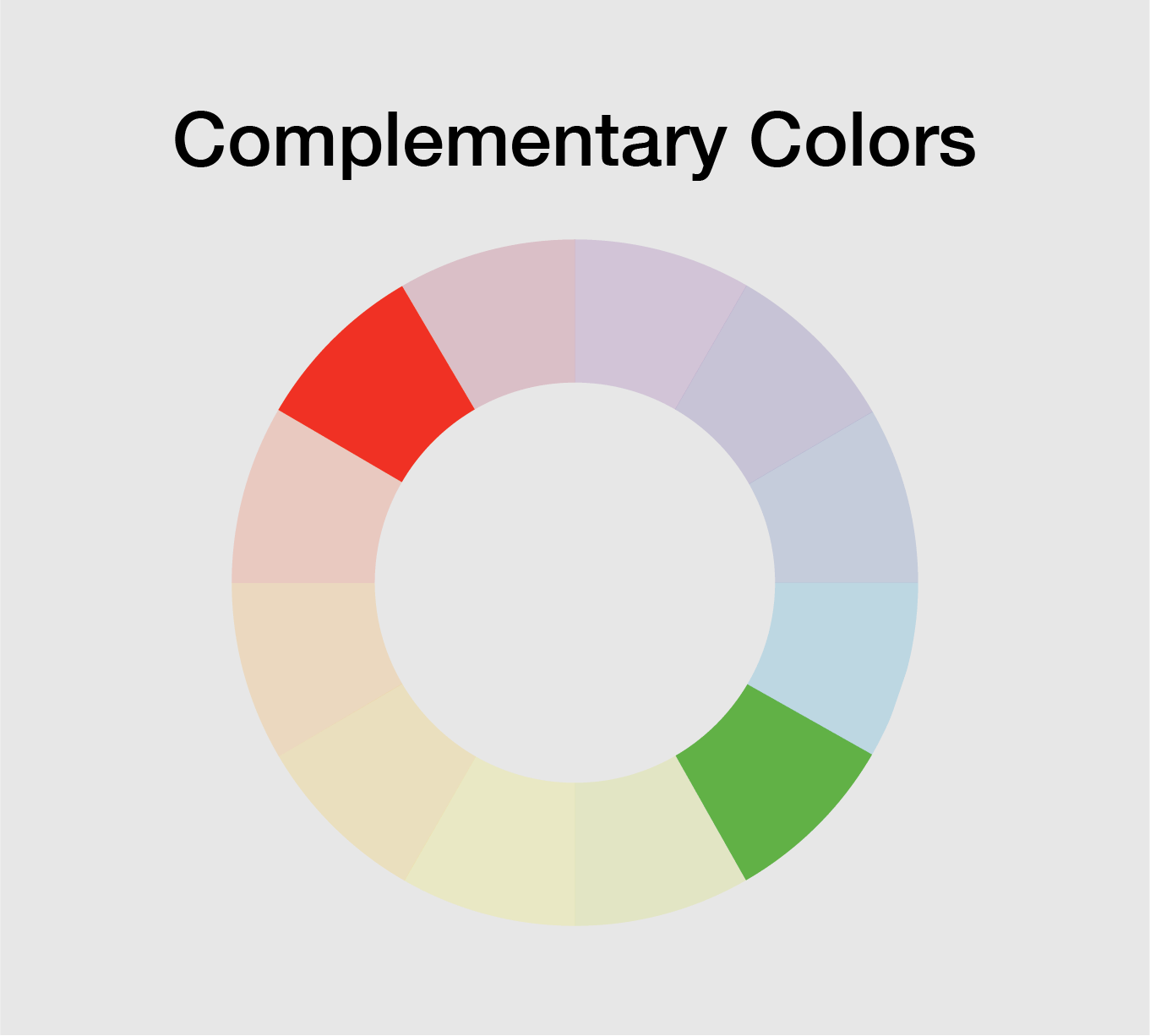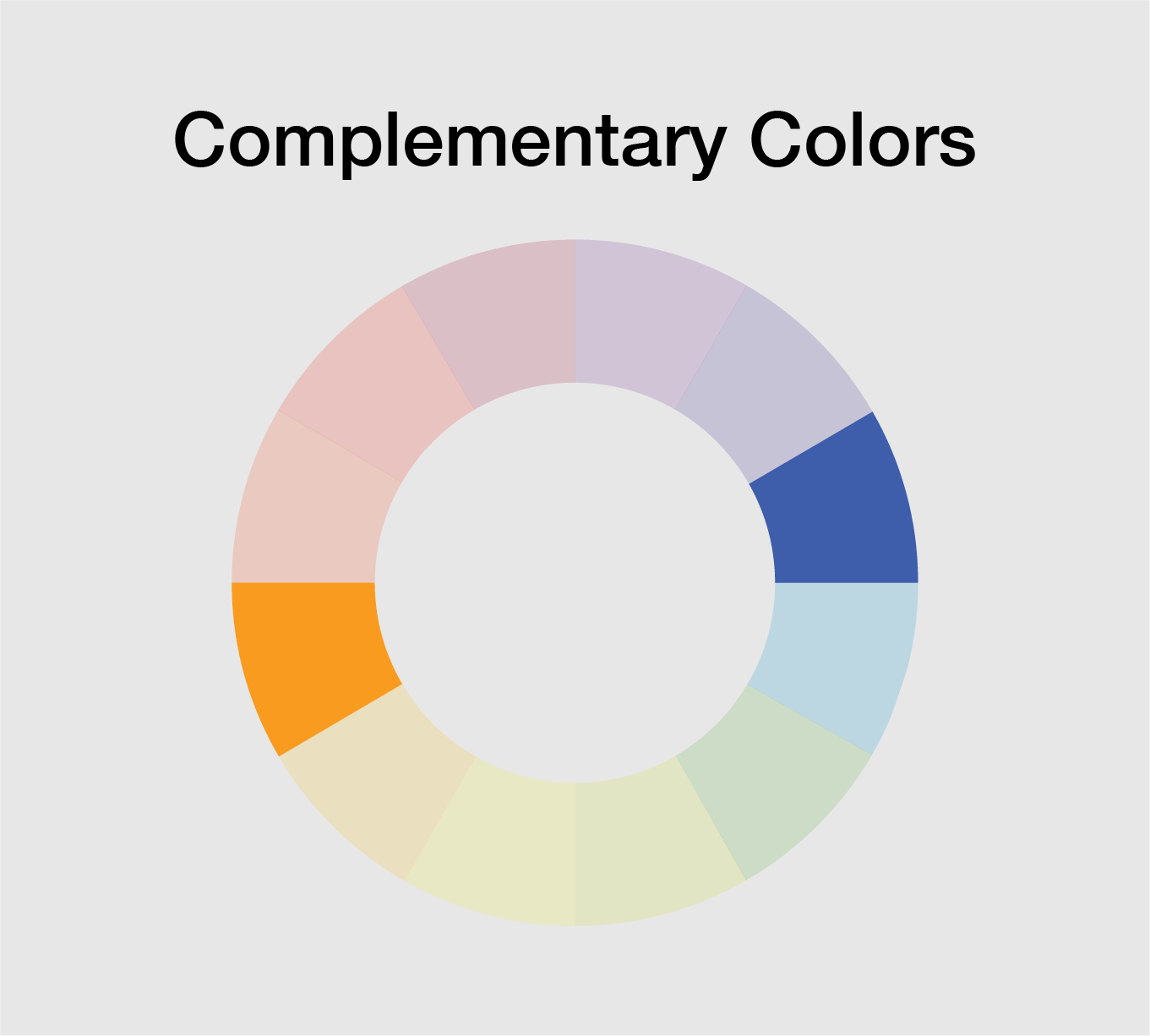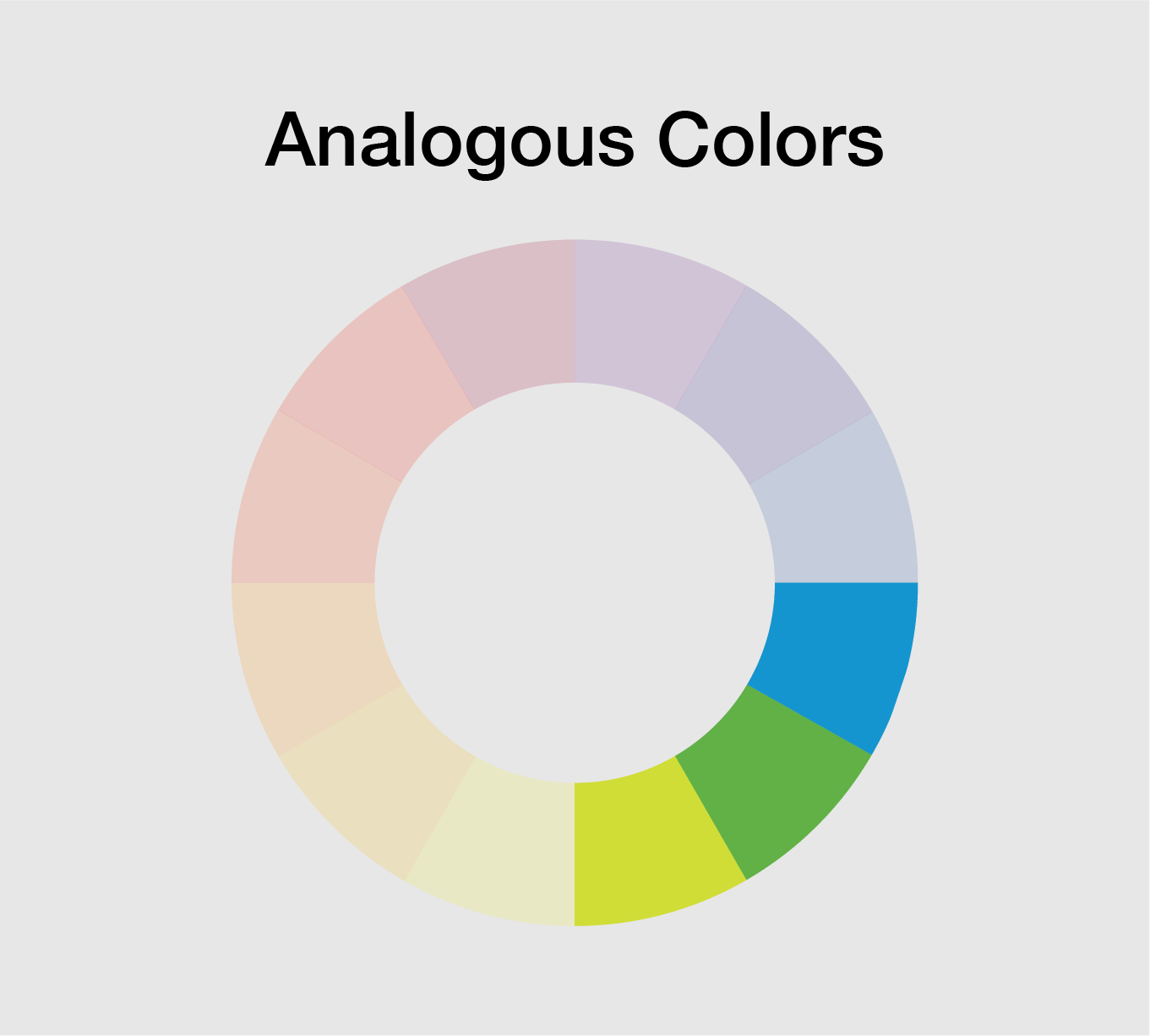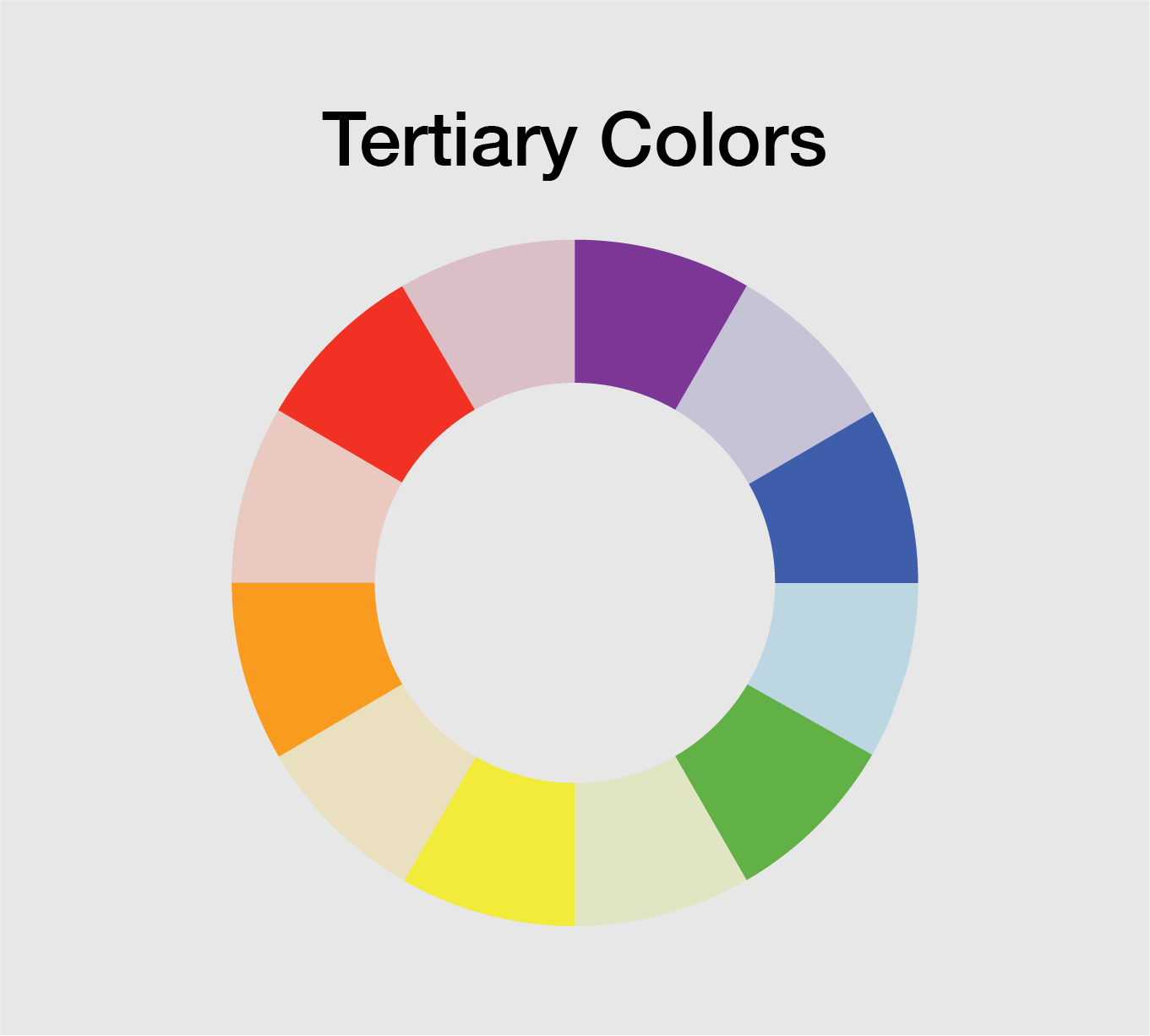
The color wheel is a visual representation of the relationships between colors. It is a tool that artists and designers use to create harmonious color schemes.
Complementary colors are located opposite each other on the color wheel. When used together, they create high contrast and vibrant visual impact. Analogous colors are located next to each other on the color wheel. These color schemes create a sense of harmony and are pleasing to the eye.
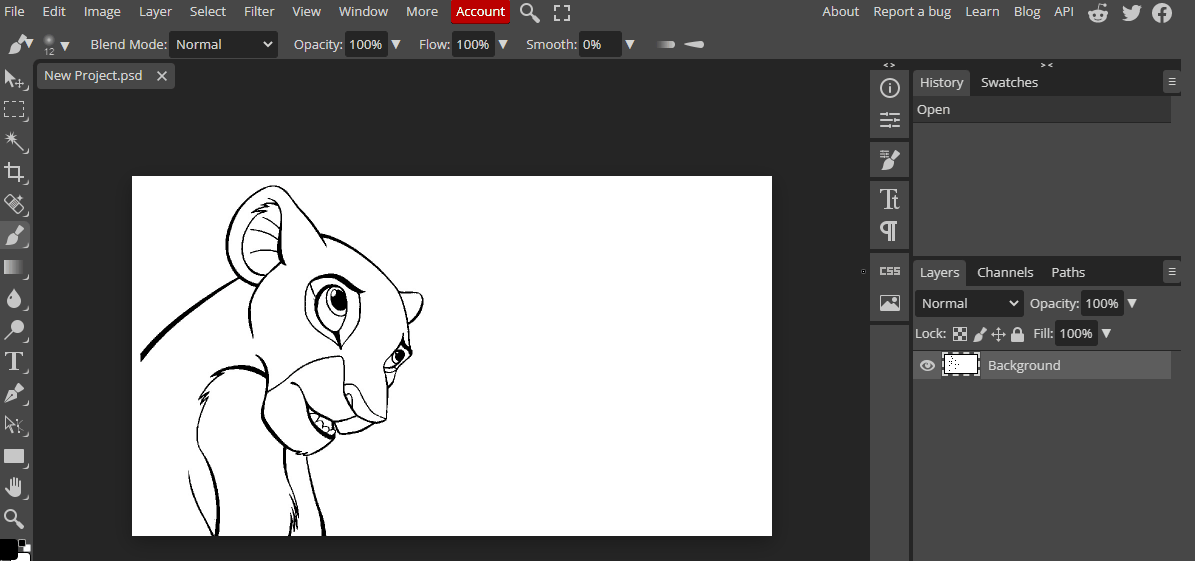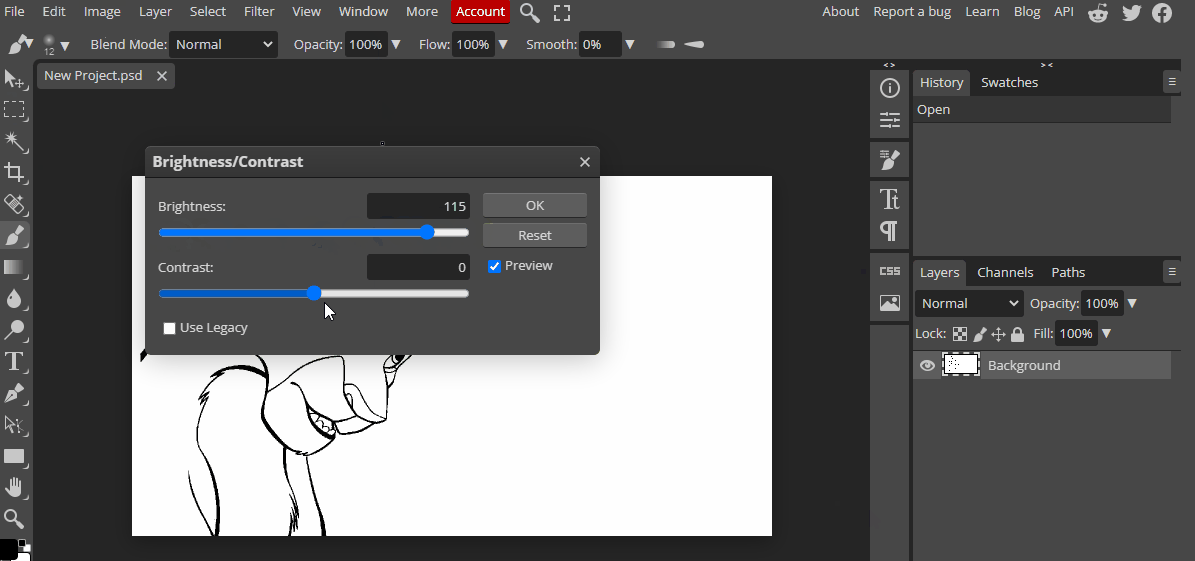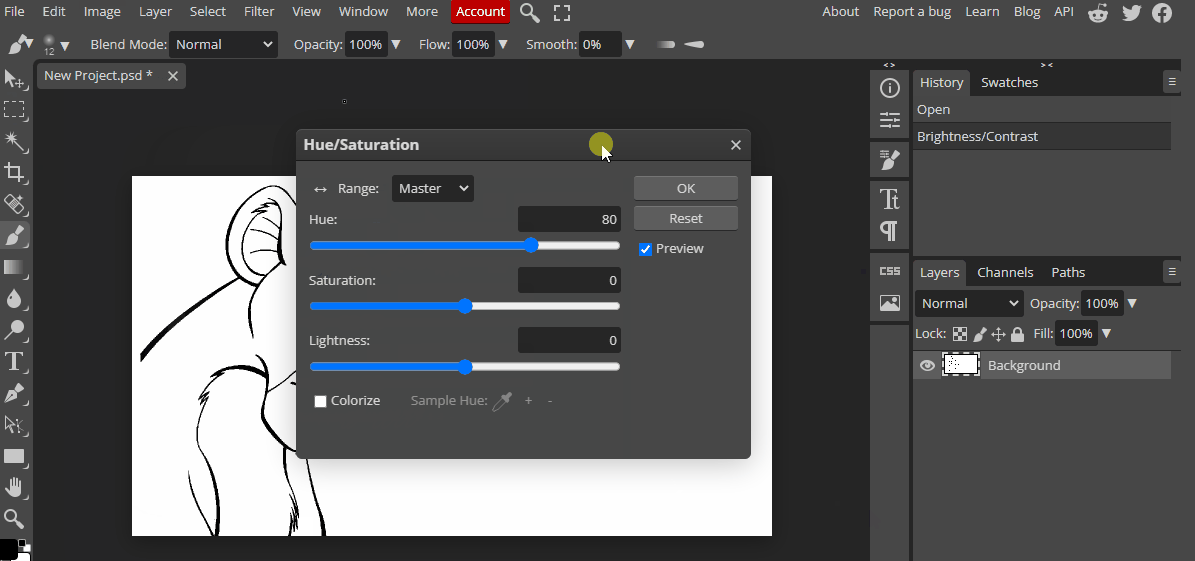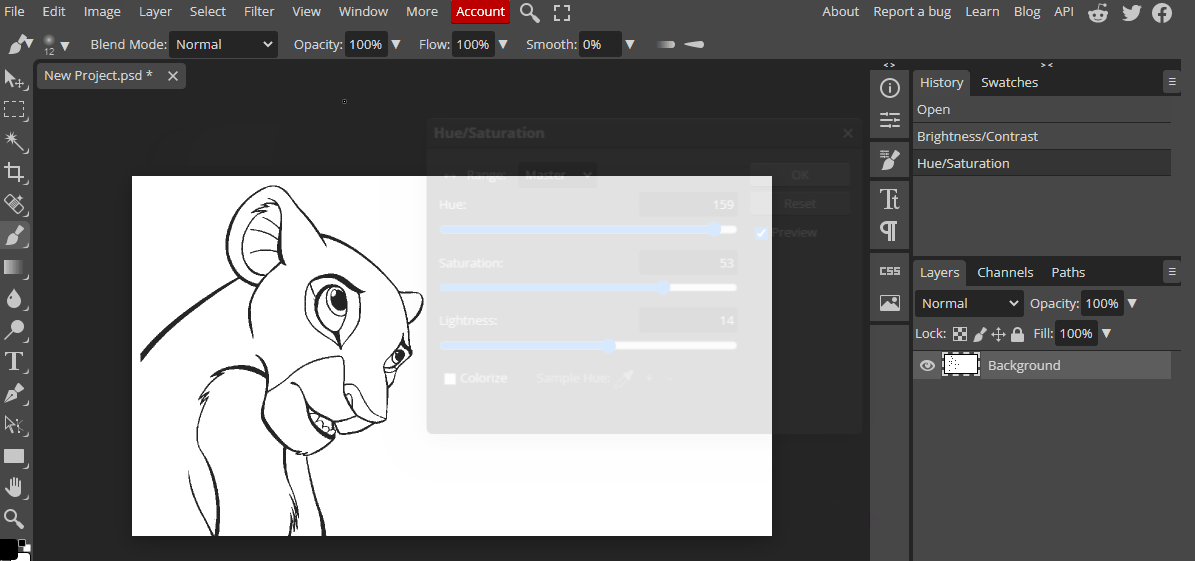
These properties are used in digital art to adjust the color and create various effects.
In Photopea, you can adjust the hue, saturation, and brightness of an image by selecting the "Hue/Saturation" adjustment layer.
Contrast refers to the difference in color and brightness between two elements. In digital art, contrast is used to create visual interest and to draw the viewer's eye to a specific area. High contrast creates bold and dramatic effects, while low contrast creates a subtle and subdued effect.