 Your Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Your Introduction to Artificial IntelligenceImagine a technology that enables your smartphone to recommend the next song you might enjoy, or adjusts the difficulty of a video game to match your skill level. This is the capability of AI.
In this lesson, you will learn the definition of AI, explore examples of AI in everyday life, and consider its capabilities and limitations. By the end, you will have a foundational understanding of this important technology.
Reflect on any 'smart' devices or applications you have encountered. For example, consider how you might ask a voice assistant like Siri a question, or receive personalised video recommendations on platforms such as YouTube.
 Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Understanding Artificial IntelligenceArtificial Intelligence, commonly abbreviated as AI, refers to the branch of computer science that focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks which typically require human intelligence. These tasks include activities such as recognising speech, making decisions, solving problems, and understanding natural language.
In essence, AI involves the development of computer programs that can process information, learn from it, and adapt their behaviour accordingly. Unlike traditional software, which follows a fixed set of instructions without change, AI systems use data to identify patterns and improve their performance over time. It is important to note that AI is not a living entity; it simulates intelligent behaviour through advanced programming and algorithms.
Artificial Intelligence is when computers or machines are built to do tasks that normally need human thinking. This can include learning from experience, solving problems, understanding language, or making decisions. In simple terms, AI helps machines act “smart.”
But let’s be clear—AI doesn’t mean robots taking over the world like in sci-fi movies. Most AI today isn’t a walking, talking robot. Instead, it’s software that works quietly in the background of apps and websites we use every day. What makes AI different from normal computers is that it can improve over time by learning from data. The more it sees, the better it gets at guessing or helping.
Artificial Intelligence is integrated into many aspects of our daily routines, often without us noticing. In this step, you will explore common examples of AI and reflect on how it appears in your own experiences.
Below are some examples of AI in action:
 The Basics of How AI Works
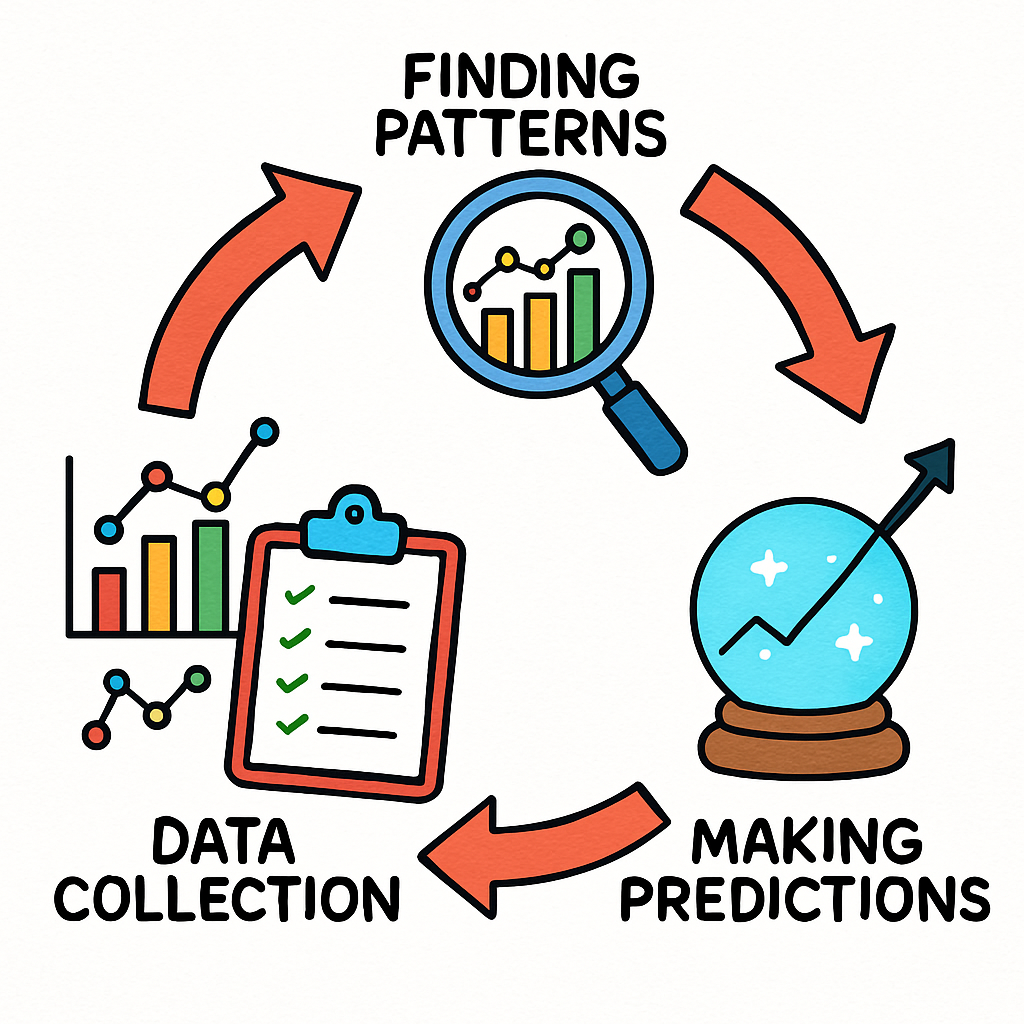
The Basics of How AI WorksArtificial Intelligence operates by processing large amounts of data to identify patterns and make informed predictions. This process is fundamental to many AI systems and can be broken down into key stages. In this step, you will learn about these stages in a structured way.
To understand AI better, consider it as a system that learns from examples, much like how you might learn a new skill through practice and observation. However, AI relies on algorithms – sets of rules and calculations – to achieve this. There is no magic involved; it is all based on careful programming and data analysis.
This cycle of collecting data, finding patterns, and making predictions allows AI to improve over time, a concept known as machine learning. Remember, the more high-quality data an AI system has, the more accurate its predictions become.
Look at each image and decide whether it's real or AI-generated. Click your answer to find out and then move on to the next image.